Introduction:
Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide, claiming millions of lives each year. While there are various types of heart diseases, some pose a higher risk and are considered the most dangerous. Understanding these conditions, their causes, and the preventive measures is crucial for maintaining heart health. In this article, we will explore the most dangerous heart diseases, their implications, and strategies for prevention.
The Impact of Heart Disease
Heart disease encompasses a range of conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels, leading to serious health consequences. It can manifest in various forms, including coronary artery disease, heart attacks, congestive heart failure, and arrhythmias. Heart diseases have a significant impact on mortality rates and quality of life, making it vital to be aware of their dangers and take proactive measures for prevention.
2. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
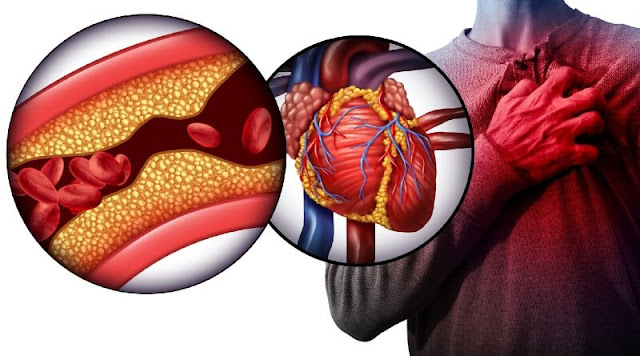
Coronary artery disease is the most common and dangerous heart disease, characterized by the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. This restriction of blood flow can lead to serious complications, including heart attacks and heart failure.
2.1. Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of coronary artery disease is the buildup of plaque, a fatty substance, inside the arteries. This process, known as atherosclerosis, occurs due to factors like high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, obesity, diabetes, and a sedentary lifestyle.
2.2. Symptoms and Complications
In the early stages, coronary artery disease may be asymptomatic. However, as the condition progresses, symptoms like chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, fatigue, and irregular heartbeats may occur. Severe complications include heart attacks, heart failure, and even sudden cardiac death.
2.3. Prevention and Treatment
Prevention and management of coronary artery disease involve adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, managing stress, and controlling underlying risk factors such as high blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Medications, surgical interventions like angioplasty or bypass surgery, and lifestyle modifications are common treatments for CAD.
3. Heart Attack
A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when the blood supply to a part of the heart is completely blocked, usually due to a blood clot. It is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention.
3.1. Causes and Risk Factors
The leading cause of heart attacks is coronary artery disease. Risk factors include a history of CAD, smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle. Family history and age also play a significant role.
3.2. Symptoms and Complications
The common symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, pain radiating to the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach, and cold sweats. Complications can be severe and include heart failure, arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac arrest.
3.3. Prevention and Treatment
Prevention of heart attacks involves managing the risk factors associated with coronary artery disease. This includes lifestyle modifications, medications to control blood pressure and cholesterol, and interventions such as angioplasty or bypass surgery. Immediate medical attention is crucial during a heart attack to restore blood flow and minimize heart damage.
4. Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
Congestive heart failure occurs when the heart muscle weakens and becomes unable to pump blood effectively. It leads to a buildup of fluid in the body and affects the overall functioning of organs.
4.1. Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of congestive heart failure can include coronary artery disease, heart attacks, high blood pressure, heart valve diseases, certain infections, and conditions like diabetes and obesity.
4.2. Symptoms and Complications
Common symptoms of congestive heart failure include fatigue, shortness of breath, swelling in the legs and ankles, rapid weight gain, and persistent coughing or wheezing. Complications include fluid accumulation in the lungs, kidney problems, and an increased risk of heart attacks.
4.3. Prevention and Treatment
Prevention and management of congestive heart failure involve lifestyle changes such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, weight management, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption. Medications, including diuretics and ACE inhibitors, may be prescribed to manage symptoms and improve heart function. In severe cases, heart transplantation may be necessary.
5. Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms that can occur due to various factors, including heart disease, electrolyte imbalances, certain medications, and genetic predisposition. Some arrhythmias can be life-threatening.
5.1. Causes and Risk Factors
Common causes of arrhythmias include coronary artery disease, heart attacks, heart failure, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, excessive alcohol or caffeine consumption, and drug abuse.
5.2. Symptoms and Complications
Arrhythmias can manifest as palpitations, rapid heartbeat, chest discomfort, dizziness, fainting, and shortness of breath. Severe arrhythmias can lead to complications such as stroke, heart failure, or sudden cardiac arrest.
5.3. Prevention and Treatment
Prevention strategies for arrhythmias involve managing underlying heart conditions, avoiding triggers such as excessive alcohol or caffeine, and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle. Treatment options include medications, cardiac devices like pacemakers or defibrillators, and procedures like ablation to correct the abnormal heart rhythm.
6. Prevention Strategies for Heart Health
While these heart diseases pose significant risks, prevention is key to maintaining heart health. Some general preventive measures include:
Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet, engage in regular physical activity, manage stress, avoid smoking, and limit alcohol consumption.
Regular health check-ups: Monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar regularly. Detecting and managing these risk factors early can prevent the development of dangerous heart diseases.
Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity is a significant risk factor for heart disease. Aim to achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Managing stress: Chronic stress can contribute to heart disease. Incorporate stress-reducing activities into your routine, such as meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy.
Avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke: Smoking is a major cause of heart disease. Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke significantly reduce your risk.
It’s important to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice on preventive measures based on your specific health profile and medical history.
Conclusion:
Understanding the most dangerous heart diseases is crucial for recognizing the risks and taking proactive steps to prevent them. Coronary artery disease, heart attacks, congestive heart failure, and arrhythmias are among the most serious conditions affecting the heart. By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, managing risk factors, and seeking regular medical care, you can significantly reduce your chances of developing these dangerous heart diseases. Remember, prevention is key when it comes to heart health, and early detection and treatment are vital for better outcomes.
By prioritizing your cardiovascular health and making informed choices, you can work towards a healthier heart and enjoy a better quality of life
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are the most dangerous heart diseases?A: The most dangerous heart diseases include coronary artery disease (CAD), heart attacks, congestive heart failure (CHF), and arrhythmias.
Q2: How can I prevent heart disease?A: To prevent heart disease, adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle, manage risk factors like high blood pressure and cholesterol, avoid smoking, maintain a healthy weight, and seek regular medical care.
Q3: What are the symptoms of a heart attack?A: Symptoms of a heart attack may include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, pain radiating to the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach, and cold sweats. If you experience these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
Q4: Can heart disease be cured?A: While heart disease cannot always be cured, it can be managed through lifestyle changes, medications, and medical interventions. Early detection and treatment are crucial for better outcomes.
Q5: How often should I have my heart health checked?A: Regular health check-ups with your healthcare provider are recommended, especially if you have risk factors for heart disease. Monitoring blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar regularly can help detect and manage potential issues.